Table of Contents
Know somatic (Somatoform) symptom disorder
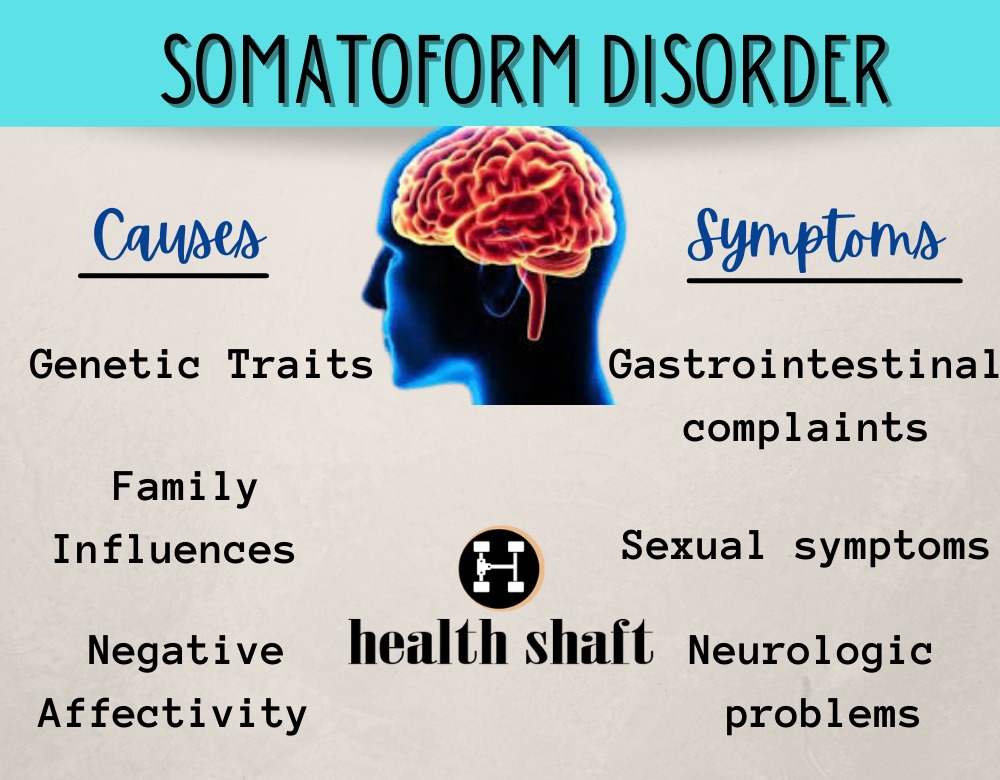
Briquette’s syndrome was named after Paul Briquette, who initially identified sanitization illness in 1859.A somatic symptom disorder, formerly known as a somatoform disorder, is any mental disorder that manifests as physical symptoms that suggest illness or injury, but which cannot be fully explained by a general medical condition or the direct effect of a substance, and which are not attributable to another mental disorder.
Types of somatoform disorder
There are seven categories of somatoform diseases, in which people have a wide range of clinically important symptoms that they can’t explain, such as:
1. Somatization disorder.
Somatization disorder is a mental and behavioral illness defined by recurrent, numerous, and present complaints about somatic symptoms that are clinically severe. It was recognized in the DSM-IV-TR categorization system, but it was merged with undifferentiated somatoform disorder to become somatic symptom disorder, a diagnosis that no longer required a fixed number of somatic symptoms.
2. Conversion disorder.
Conversion disorder is a condition in which a person develops blindness, paralysis, or other nervous system symptoms that are not caused by a medical illness or injury. The body’s reaction to a traumatic physical or emotional experience is regarded to be the origin of conversion disorder.
3. Pain disorder.
When pain cannot be explained by a medical or other illness, when pain causes significant distress, and when psychological variables play a significant role in the onset, size, and duration of the pain, a pain disorder diagnosis is made.
4. Hypochondriasis.
Hypochondriasis, often known as hypochondria, is a condition in which a person is too concerned about a dangerous illness. When a person has hypochondriasis, he or she feels that typical physical indicators or modest symptoms indicate a serious illness, despite medical tests and evaluations proving otherwise.
5. Other specified somatic symptom and related disorder.
Other Specified Somatic Symptom Disorders is a DSM-5 diagnosis that applies to people who experience symptoms that are similar to those of a somatic symptom or related disorder (e.g., somatic symptom disorder, sickness anxiety disorder) but don’t fulfill all of the criteria for any of them.
6. Unspecified somatic symptom and related disorder.
Undifferentiated somatoform disorder, like particular somatic symptom and related illnesses, refers to people who show symptoms of somatic disorders but don’t fit the full criteria for any somatoform condition. These symptoms, however, cannot be linked to a specific physical cause.
- Body dysmorphic disorder.
Body dysmorphic disorder is a mental health condition that causes you to obsess over one or more perceived deficiencies in your appearance. You obsess over your appearance and body image if you have body dysmorphic disorder, checking the mirror, grooming, and seeking reassurance frequently throughout the day, often for several hours.
Somatic symptom disorder test
You’ll most likely undergo a physical exam and whatever tests your doctor prescribes to obtain a diagnosis. If you have any health issues that require treatment, your doctor or other health care professional can assist you.
The PHQ-15, WI-7, and SAIB are all good screening tools for detecting people who are at risk for somatic symptom disorder, and using all three together enhances diagnosis accuracy marginally. Improved identification rates for somatic symptom disorder will result from their usage in routine care.
A mental health professional may be referred to you by your medical care provider, who may:
Discuss your symptoms, anxieties, and concerns, stressful events, interpersonal issues, scenarios you may be avoiding and family history during a psychological examination.
Have you completed a psychological questionnaire or self-assessment?
Inquire about your usage of alcohol, drugs, or other substances.
Somatic symptom disorder treatment
Treatment aims to improve your symptoms as well as your capacity to operate in everyday life. Psychotherapy, often known as talk therapy, can help with somatic symptom disorder.
Rather of treating symptoms, treatment focuses on improving everyday functioning. Reducing stress is frequently a key element of getting healthy. Counseling with family and friends may also be effective.
Treatment with cognitive behavioural therapy may help to relieve the symptoms of SSD. The aim of the therapy is on correcting:
Thoughts that are distorted, Unrealistic assumptions, anxiety-inducing behaviors.
CBT can also assist you in the following ways:
- Examine and adjust your health and physical symptom assumptions and expectations.
- Learn how to manage your stress.
- Learn how to deal with bodily manifestations.
- Cut down on the amount of time you think about your symptoms.
People also ask
Is somatoform disorder the same as somatic symptom disorder?
Both somatoform disorder and somatic symptom disorder are same. Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) is a kind of mental disease that causes one or more physiological symptoms, such as discomfort.
What is the difference between somatoform disorder and somatization disorder?
Somatization occurs when physical symptoms are induced by mental (psychological) or emotional elements, whereas somatoform illnesses are at the other end of the range. As a result, the physical symptoms remain for an extended period of time or are severe, but no physical ailment can adequately explain them.
What is somatoform disorder?
Somatoform disorders are a collection of mental diseases characterized by a wide range of clinically relevant but unexplained physical symptoms. Among the somatoform disorders include somatization disorder, undifferentiated somatoform disorder, hypochondriasis, conversion disorder, pain disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, and undefined somatoform disorder.
What are examples of somatic complaints? OR What is an example of a somatic disorder?
Examples of somatic complaints are specific feelings like pain or shortness of breath, as well as more general symptoms like exhaustion and weakness.
Unrelated to any identifiable medical reason, or connected to a medical problem such as cancer or heart disease, but more substantial than predicted.
A single symptom, a group of symptoms, or a series of symptoms.
Mild, moderate, or severe are the three levels of severity.
What are somatic symptoms of anxiety?
Abdominal discomfort, dyspepsia, chest pain, exhaustion, dizziness, sleeplessness, and headache are common symptoms of somatization of anxiety and other mental diseases.
What are somatic symptoms of trauma?
Past trauma scars frequently emerge in various somatic symptoms in addition to emotional distress and physical harm. Patients may experience weariness, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, joint or muscle discomfort, headaches, and palpitations, all of which may or may not be transient.
What is somatic personality disorder?
When a person experiences severe, exaggerated concern over bodily symptoms, this is known as somatic symptom disorder (SSD). The individual has such strong thoughts, feelings, and actions in response to the symptoms that they believe they are unable to do some daily activities.
Conclusion
The included studies have a lot of statistical heterogeneity. Somatoform disorders and medically unexplained symptoms are far more frequent than most people think. The prevalence rates discovered emphasize the relevance of these illnesses in primary care.